Petri Net Capability Integration in MS Visio should considered.
Here is a copy of a short description from a discontinued project:
FMC Petri Nets - Dynamic Structures
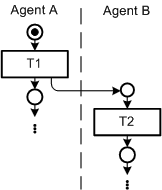
FMC diagrams for dynamic structures are based on transition-place Petri nets. They are used to express system behavior over time, depicting the actions performed by the agents. So they clarify how a system is working and how communication takes place between different agents.
| Basic Elements | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
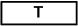 | transition | Stands for an operation, an event or an activity. (Note: verb should be used for identifier "T") | |||||||||
 | unmarked and marked place | A place represents a control state or an additional condition. It may be marked, i.e. it holds a token. (Note: here capacity = 1, i.e. a place cannot hold more than one token at the same time) | |||||||||
 | directed arc | Connects a place and a transition. (Note: here arc weight = 1, i.e. exactly one token will be consumed or produced when the connected transition fires) | |||||||||
| Further Elements | |||||||||||
 | NOP | A transition meaning No OPeration. (Note: often used to preserve the bipartiteness) | |||||||||
 | swimlane divider | Distinguishes competences of agents. | |||||||||
| Common Structures | |||||||||||
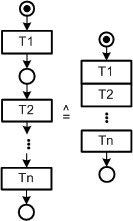
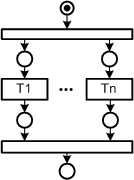
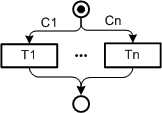
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Extended Elements | |||||||||||
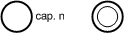 | multi-token place | Places which can hold multiple tokens but not an infinite number are indicated as enlarged places with an annotation specifying the capacity (n>1). Places with an infinite capacity are indicated by double a circle. | |||||||||
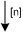 | directed arc | The arc weight n determines how much tokens will be consumed or produced when the connected transition fires. An arc weight of 1 is assumed, if there is no one specified. | |||||||||
| Recursion Elements | |||||||||||
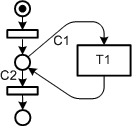
 | stack place | Is a place to store information about return positions using stack tokens. All stack places with the same name are strongly coupled with each other as the stack tokens, although placed on several stack places, are managed in a single stack. So all the stack places together constitute the return stack. | |||||||||
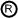 | return place | Is used like a normal place. But there is always a conflict to solve as a return place is an input place for at least two transitions that also have stack places as input places. When a return place gets a token and more than one associated stack places have a stack token the conflict is always solved in the same manner: the newest token on the stack must be consumed first. The newest token belongs to exactly one stack place and so the transition where this stack place is an input place will fire. | |||||||||
| General Recursion Scheme | |||||||||||
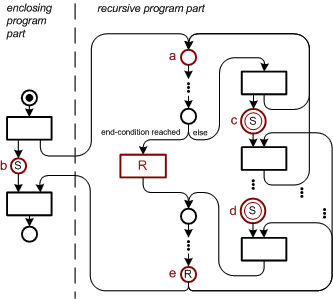 | Each recursive diagram shows the following characteristics:
| ||||||||||